PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
EINECS NO.
H.S.CODE
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.npi.gov.au/
Australia-National
Pollutant Inventory: Copper & compounds: Overview
Local: Copper forms compounds in the oxidation states +1 and +2 ( trivalent copper survives no more than a few seconds in an aqueous solution). Copper Carbonate is the common name for the green crystalline cupric carbonate, in which copper has valence +2. It is soluble in water and decomposes at 200 C. It is used in paint and varnish pigments, pyrotechnics and animal and poultry feeds It is also used as a fungicide. In chemical industry, it is used in manufacturing other copper salts as well as an antidote for phosphorous poisoning.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF COPPER COMPOUNDS: Copper forms compounds in the oxidation states of +1 (cuprous) and +2 (cupric); trivalent copper survives no more than a few seconds in an aqueous solution. The relatively small change in electrochemical potential between the cuprous and cupric ions in solution gives the usefulness of copper compounds in chemical reactions. Copper compounds are used as catalysts in reactions, especially oxidation (cupric chloride) and heterogeneous reactions. Cupric chloride, copper chloride (CuCl2) is a yellowish to brown, deliquescent powder; soluble in water, alcohol, and ammonium chloride; while the dihydrated form of cupric chloride is a green crystals; soluble in water. It is used as a mordant in dyeing and printing textile fabrics and in the refining of copper, gold, and silver as well as a catalyst in chemical reactions. Cuprous chloride (CuCl or Cu2Cl2), also known as resin of copper, is a green, tetrahedral crystals; insoluble in water. The biological property of copper compounds takes important role in as fungicides in agriculture and biocides in antifouling paints for ships and wood preservations. Very low level of copper is toxic to fungi and algae but the levels for mammal is much higher. The copper ions inhibit the metabolism of the fungus when they react with sulfur containing enzymes in the plant. Copper compounds form a protective barrier on the plant surface and thereby prevent fungi from entering the plant host. The fungicidal effect of copper compounds as non-systemic fungicides are such as bordeaux mixture, cupric hydroxide, copper arsenate, copper carbonate, cuprous oxide, copper-8-quinolinolate, copper oleate, copper sulfate, or copper oxychloride. Another important biological application of copper compounds, such as copper sulfide is as an antifouling agent in paints. The description and applications of copper compounds in industry are;- Copper Arsenate, Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O; bluish powder which is insoluble in water and alcohol, soluble in ammonium hydroxide and dilute acids; used as a fungicide and insecticide.
- Copper Arsenite, also known as Scheele's green, CuHAsO3 ; toxic, green powder which is soluble in acids and decomposes at the melting point; used as a pigment and insecticide;
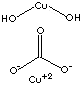
- Copper Carbonate, artificial malachite. Cu2(OH)2CO3, toxic, green powder which is soluble in acids and decomposes at 200 C; used in pigments and pyrotechnics and as a fungicide and feed additive; antidote for phosphorous poisoning.
- Copper Gluconate [CH2OH(CHOH)4COO]2Cu. light blue, crystalline powder which is soluble in water; used in medicine and as a dietary supplement; scale removal in metal cleanings and can be formulated in cleaning compounds including mouthwash due to its sequestering ability in alkaline conditions.
- Copper Oleate Cu[OOC(CH2)7CHCH(CH2)7CH3]2 , green to blue liquid, used as a fungicide for fruits and vegetables; used in formulating antiseptics, deodorants, antiperspirants.
- Copper-8-Quinolinolate C18H14N2O2Cu, khaki-colored solid which is insoluble in water; used as a fungicide in fruit and vegetables equipments.
- Copper Sulfide CuS, black, monoclinic or hexagonal crystals which decomposes at 220 C; used antifouling agent in paints.
- Cupric Acetate (Copper Acetate), known as crystals of Venus, Cu(C2H3O2)2·H2O, blue to green crystals which is soluble in water; used as a raw material to make paris green; organic reaction catalyst; textile dyeing; fungicide.
- Cupric Bromide (Copper Bromide) CuBr2, black prismatic crystals; used in photography as an intensifier and in organic synthesis as a brominating agent.
- Cupric Chloride (copper chloride) CuCl2, yellowish to brown, deliquescent powder which is soluble in water, alcohol, and ammonium chloride; used as a mordant in dyeing and printing textile fabrics and in the refining of copper, gold, and silver.
- Cupric Chromate (Copper Chromate) CuCrO4, yellow liquid used as a mordant.
- Cupric Cyanide (Copper Cyanide) Cu(CN)2, green powder which is insoluble in water; used in electroplating copper on iron.
- Cupric Fluoride (Copper Fluoride) CuF2, white crystalline powder used in ceramics and in the preparation of brazing and soldering fluxes.
- Cupric Hydroxide (Copper Hydroxide) Cu(OH)2, blue microscopic crystals; used as a mordant and pigment, in manufacture of many copper salts, and for staining paper.
- Cupric Nitrate (Copper Nitrate) Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, green powder or blue crystals which is soluble in water; used in electroplating copper on iron; as a catalyst and nitrating agent in organic reactions; component in rocket fuel; fungicides and wood preservatives; textile dyeing and printing; pigment in ceramics;
- Cupric Oxide (Copper Oxide) CuO, black, monoclinic crystals which is insoluble in water; used in making fibers and ceramics; in organic and gas analyses; catalyst, fungicide, antiseptic; red pigment for glass, ceramics; antifouling gent;
- Cuprous Bromide (Copper Bromide) Cu2Br2, white or gray crystals slightly soluble in cold water.
- Cuprous Chloride (Copper Chloride) CuCl or Cu2Cl2, green, tetrahedral crystals which is insoluble in water; used as a heat and light stabilizer for nylon and as a catalyst for chemical synthesis. used as a crude for phthalocyanine blue pigments; used as desulfuring agent in the refinery industry
- Cuprous Fluoride (Copper Fluoride) Cu2F2, red crystalline powder which melts at 908 C.
- Cuprous Oxide (Copper Oxide) Cu2O, an oxide of copper found in nature as cuprite and formed on copper by heat; used chiefly as a pigment and as a fungicide; soil additive; colorant in ceramics; electroplating baths; petroleum industry;
Copper sulfate is the common name for the blue crystalline cupric sulfate, in which copper has valence +2. It may also refer to cuprous sulfate (Cu2SO4), in which copper has valence +1. It is soluble in water but insoluble in alcohol. It usually crystallizes as a pentahydrate compound containing five molecules of water (CuSO4·5H2O) and is known in commerce as blue vitriol. It is prepared by the treatment of copper oxides with sulfuric acid. Cupric sulfate is the most important salt of copper. Cupric sulfate is utilized chiefly for agricultural purposes, as a pesticide, germicide, feed additive, and soil additive. It is also used as a raw material in the preparation of other copper compounds, electrolyte for batteries and electroplating baths, and in medicine as a locally applied fungicide, bactericide, and astringent. It also finds wide use in the preparation of pigments. Copper is an essential trace nutrient which performs a number of diverse functions in protein biochemistry. Some copper compounds such as copper sulfate are used as a supplement for livestock.
APPEARANCE
0.02% max
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H335: May cause respiratory irritation
H319: Causes
serious eye irritation
H315: Causes skin irritation
H301:
Toxic if swallowed
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray
P302+
P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water
P280:
Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face
protection
P305 + P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously
with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present
and easy to do. Continue rinsing
P264: Wash face, hands
and any exposed skin thoroughly after handling
P270: Do
not eat, drink or smoke when using this product
![]() T
Toxic
T
Toxic
RISK PHRASES
25: Toxic if swallowed.
36/37/38: Irritating to
eyes, respiratory system and skin.
SAFETY PHRASES
26: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with
plenty of water and seek medical advice.
37/39: Wear suitable
gloves and eye/face protection.
45: In case of accident
or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the
label where possible).
PRICE INFORMATION